Strand breakage of a (6–4) photoproduct-containing DNA at neutral pH and its repair by the ERCC1–XPF protein complex†
Abstract
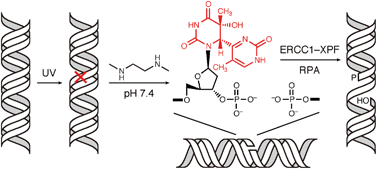
The (6–4) photoproduct is one of the major UV-induced lesions in DNA. We previously showed that hydrolytic ring opening of the 5′ base and subsequent hydrolysis of the glycosidic bond of the 3′ component occurred when this photoproduct was treated with aqueous NaOH. In this study, we found that another product was obtained when the (6–4) photoproduct was heated at 90 °C for 6 h, in a 0.1 M solution of N,N′-dimethyl-1,2-ethanediamine adjusted to pH 7.4 with acetic acid. An analysis of the chemical structure of this product revealed that the 5′ base was intact, whereas the glycosidic bond at the 3′ component was hydrolyzed in the same manner. The strand break was detected for a 30-mer oligonucleotide containing the (6–4) photoproduct upon treatment with the above solution or other pH 7.4 solutions containing biogenic amines, such as spermidine and spermine. In the case of spermidine, the rate constant was calculated to be 1.4 × 10−8 s−1 at 37 °C. The strand break occurred even when the oligonucleotide was heated at 90 °C in 0.1 M sodium phosphate (pH 7.0), although this treatment produced several types of 5′ fragments. The Dewar valence isomer was inert to this reaction. The product obtained from the (6–4) photoproduct-containing 30-mer was used to investigate the enzymatic processing of the 3′ end bearing the damaged base and a phosphate. The ERCC1–XPF complex removed several nucleotides containing the damaged base, in the presence of replication protein A.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...