The application of stop-flow microwave technology to scaling-out SNAr reactions using a soluble organic base†‡
Abstract
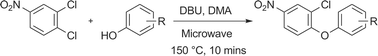
A model SNAr reaction which gives a range of substituted diaryl ethers has been re-developed to function with the soluble organic base DBU in the place of insoluble potassium carbonate. Manufacture of these diaryl ethers has then been achieved by scaling-out in an automated stop-flow microwave reactor to give productivities of >0.5 kg per day. Analogous reaction partners have also been scaled up in this reactor to extend the scope of the study. Brief comparison in a scale-up batch microwave reactor is also made. Lastly, continuous 24 h processing is reported in this small microwave stop-flow reactor, which requires no manual intervention once started.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...