Importance of the backbone conformation of (−)-ternatin in its fat-accumulation inhibitory activity against 3T3-L1 adipocytes†
Abstract
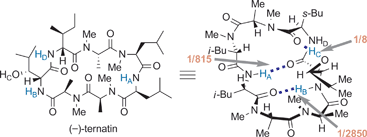
Key relationships between the intramolecular H-bond-derived backbone conformation and the bioactivity of the novel fat-accumulation

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...