Parallelized biocatalytic scanning probe lithography for the additive fabrication of conjugated polymer structures†
Abstract
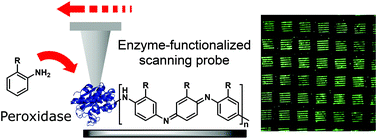
Scanning probe lithography (SPL) offers a more accessible alternative to conventional photolithography as a route to surface nanofabrication. In principle, the synthetic scope of SPL could be greatly enhanced by combining the precision of scanning probe systems with the chemoselectivity offered by biocatalysis. This report describes the development of multiplexed SPL employing probes functionalized with horseradish peroxidase, and its subsequent use for the constructive fabrication of polyaniline features on both silicon oxide and gold substrates. This polymer is of particular interest due to its potential applications in organic electronics, but its use is hindered by its poor processability, which could be circumvented by the direct in situ synthesis at the desired locations. Using parallelized arrays of probes, the lithography of polymer features over 1 cm2 areas was achieved with individual feature widths as small as 162 ± 24 nm. The nature of the deposited materials was confirmed by Raman spectroscopy, and it was further shown that the features could be chemically derivatized postlithographically by Huisgen [2 + 3] “click” chemistry, when 2-propargyloxyaniline was used as the monomer in the initial lithography step.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...