Enhanced catalytic activity for CO oxidation by the metal–oxide perimeter of TiO2/nanostructured Au inverse catalysts†
Abstract
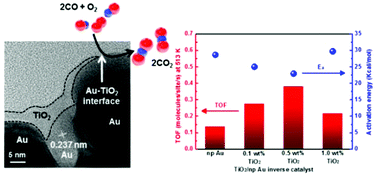
We report the effect of metal–oxide interfaces on CO oxidation catalytic activity with inverse TiO2-nanostructured Au catalysts. The inverse nanocatalysts were prepared by depositing TiO2via the liquid-phase immersion method on electrochemically synthesized Au nanostructure supports. The catalytic performance for CO oxidation was investigated using various amounts of Ti (i.e. 0.1–1.0 wt%) on two different morphologies of Au nanostructures (i.e. nanoporous and nanorod). In comparing the different Au morphologies, we found an overall higher TOF and lower activation energy for the TiO2/nanoporous Au than those for the TiO2/nanorod Au. In addition, the CO oxidation activity increased as the Ti content increased up to 0.5 wt% probably due to active TiO2–Au interface sites enhancing CO oxidation via the supply of adsorption sites or charge transfer from TiO2 to Au. However, a higher titania content (i.e. 1.0 wt% TiO2) resulted in decreased activity caused by high surface coverage of TiO2 decreasing the number of TiO2–Au interface sites. These results implied that the perimeter area of the metal–oxide interface played a significant role in determining the catalytic performance for CO oxidation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...