Ru nanoparticles dispersed on magnetic yolk–shell nanoarchitectures with Fe3O4 core and sulfoacid-containing periodic mesoporous organosilica shell as bifunctional catalysts for direct conversion of cellulose to isosorbide†
Abstract
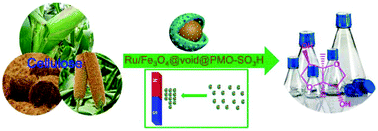
A green and sustainable approach for biorefining involves the development of bifunctional catalysts for the one-pot conversion of cellulosic biomass to isosorbide. This requires highly efficient, easily separated and versatile metal–acid catalysts for hydrolysis–hydrogenation–dehydration cascade reactions. Herein, we report a new type of metal–acid bifunctional catalyst by dispersing Ru nanoparticles (NPs) on magnetic yolk–shell nanoarchitectures comprising an Fe3O4 core and a sulfoacid (SO3H)-containing periodic mesoporous organosilica shell. The resultant magnetic Ru–SO3H nanoreactors are highly porous and have large surface areas (>350 m2 g−1), uniform mesopores (∼3.8 nm), well-dispersed Ru NPs (<1.5 wt%) and superior magnetization. Tailoring the size of the Ru NPs and the amount of SO3H moieties produced a highly efficient Ru–SO3H nanocatalyst, which delivered a high yield of isosorbide of 58.1% with almost complete conversion of cellulose in 2 h and achieved maximum productivity of 2.19 molIsosor h−1 gRu−1, which was one order of magnitude higher than that achieved using other Ru-containing acidic catalysts. Moreover, the elaborately fabricated Ru–SO3H nanocatalyst can be easily separated by applying an external magnetic field and can be cycled four times. This work reveals new possibilities for the fabrication of highly efficient, easily separated metal–acid catalysts in virtue of the concept of nanoreactor design.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...