In situ tribochemical sulfurization of molybdenum oxide nanotubes
Abstract
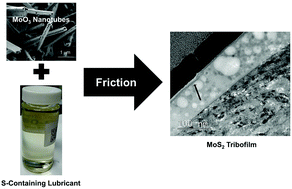
MoS2 nanoparticles are typically obtained by high temperature sulfurization of organic and inorganic precursors under a S rich atmosphere and have excellent friction reduction properties. We present a novel approach for making the sulfurization unnecessary for MoO3 nanotubes during the synthesis process for friction and wear reduction applications while simultaneously achieving a superb tribological performance. To this end, we report the first in situ sulfurization of MoO3 nanotubes during sliding contact in the presence of sulfur-containing lubricant additives. The sulfurization leads to the tribo-chemical formation of a MoS2-rich low-friction tribofilm as verified using Raman spectroscopy and can be achieved both during sliding contact and under extreme pressure conditions. Under sliding contact conditions, MoO3 nanotubes in synergy with sulfurized olefin polysulfide and pre-formed zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate tribofilms achieve an excellent friction performance. Under these conditions, the tribochemical sulfurization of MoO3 nanotubes leads to a similar coefficient of friction to the one obtained using a model nanolubricant containing MoS2 nanotubes. Under extreme pressure conditions, the in situ sulfurization of MoO3 nanotubes using sulfurized olefin polysulfide results in a superb load carrying capacity capable of outperforming MoS2 nanotubes. The reason is that while MoO3 nanotubes are able to continuously sulfurize during sliding contact conditions, MoS2 nanotubes progressively degrade by oxidation thus losing lubricity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...