Efficient intracellular delivery of biomacromolecules employing clusters of zinc oxide nanowires†
Abstract
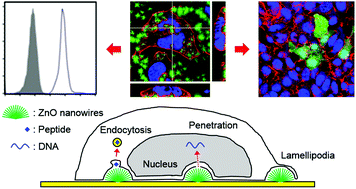
Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanocomposites have been widely applied in biomedical fields due to their multifunctionality and biocompatibility. However, the physicochemical properties of ZnO nanocomposite involved in nano–bio interactions are poorly defined. To assess the potential applicability of ZnO nanowires for intracellular delivery of biomolecules, we examined the dynamics of cellular activity of cells growing on densely packed ZnO nanowire arrays with two different physical conformations, vertical (VNW) or fan-shaped (FNW) nanowires. Although a fraction of human embryonic kidney cells cultured on VNW or FNW underwent rapid apoptosis, peaking at 6 h after incubation, cells could survive and replicate without significant apoptosis on the foreign substrate after 12 h of lag phase. In addition, the cells formed lamellipodia to wrap FNW, and efficiently took up peptides non-covalently coated on VNW and FNW within 30 min of incubation. Moreover, FNW could mediate intracellular delivery of associated DNAs and their gene expression, suggesting that ZnO nanowires transiently penetrate membranes to mediate intranuclear delivery of exogenous DNA. These results indicate that ZnO nanowire arrays can serve as nanocomposites for manipulating nano–bio interfaces if appropriately modified in a 3-dimensional conformation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...