The effects of exfoliation, organic solvents and anodic activation on the catalytic hydrogen evolution reaction of tungsten disulfide†
Abstract
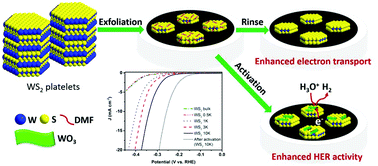
The rational design of transition metal dichalcogenide electrocatalysts for efficiently catalyzing the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) is believed to lead to the generation of a renewable energy carrier. To this end, our work has made three main contributions. At first, we have demonstrated that exfoliation via ionic liquid assisted grinding combined with gradient centrifugation is an efficient method to exfoliate bulk WS2 to nanosheets with a thickness of a few atomic layers and lateral size dimensions in the range of 100 nm to 2 nm. These WS2 nanosheets decorated with scattered nanodots exhibited highly enhanced catalytic performance for HER with an onset potential of −130 mV vs. RHE, an overpotential of 337 mV at 10 mA cm−2 and a Tafel slope of 80 mV dec−1 in 0.5 M H2SO4. Secondly, we found a strong aging effect on the electrocatalytic performance of WS2 stored in high boiling point organic solvents such as dimethylformamide (DMF). Importantly, the HER ability could be recovered by removing the organic (DMF) residues, which obstructed the electron transport, with acetone. Thirdly, we established that the HER performance of WS2 nanosheets/nanodots could be significantly enhanced by activating the electrode surface at a positive voltage for a very short time (60 s), decreasing the kinetic overpotential by more than 80 mV at 10 mA cm−2. The performance enhancement was found to arise primarily from the ability of a formed proton-intercalated amorphous tungsten trioxide (a-WO3) to provide additional active sites and favourably modify the immediate chemical environment of the WS2 catalyst, rendering it more favorable for local proton delivery and/or transport to the active edge site of WS2. Our results provide new insights into the effects of organic solvents and electrochemical activation on the catalytic performance of two-dimensional WS2 for HER.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...