Nanotopography featured polycaprolactone/polyethyleneoxide microfibers modulate endothelial cell response†
Abstract
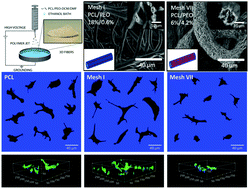
Among many physical properties, surface nanotopography has been found to strongly affect cell adhesion, migration and other functions. Accurate biological interpretation requires the nanotopography to be presented in a three-dimensional (3D) micro-environment. Herein, immiscible blends of polycaprolactone (PCL)/polyethyleneoxide (PEO) were electrospun into a grounded coagulation bath, resulting in macroporous microfibers with nanotopography featured surfaces. Variations in PCL/PEO ratios enabled tunable surface nanotopographic structures, from longitudinal submicron grooves to transverse nano-lamellae. Chemical composition, crystallinity and quantitative nanomechanical analysis confirmed that the interplay of the two semi-crystalline immiscible polymers and the pairing of miscible solvents/non-solvents in both the electrospinning solution and the bath solution were critical for the formation of the secondary structure. It was found that the nanotopography features promoted the proliferation of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) compared with their smooth film counterparts. An analysis of the cell adhesion related markers, vinculin and phosphorylated focal adhesion kinase (pFAK), further revealed that the nanotopographies enhanced the nascent adhesion complex formation compared with smooth PCL fibers, even in the scaffolds with a high PEO content, which is often considered as a non-adhesive material.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...