Crab-shell induced synthesis of ordered macroporous carbon nanofiber arrays coupled with MnCo2O4 nanoparticles as bifunctional oxygen catalysts for rechargeable Zn–air batteries†
Abstract
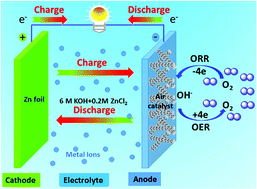
The oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER) are traditionally carried out using noble metals (such as Pt) and metal oxides (such as RuO2 and IrO2) as catalysts, respectively. Nevertheless, several key issues such as high cost, poor stability, and detrimental environmental effects limit the catalytic activity of these noble metal- and metal oxide-based catalysts. Herein, we have designed and synthesized macroporous carbon nanofiber arrays by using a natural crab shell template. Subsequently, spinel MnCo2O4 nanoparticles were embedded into the nitrogen-doped macroporous carbon nanofiber arrays (NMCNAs) by a hydrothermal method. Accompanied by the good conductivity, large surface area and doping of nitrogen, the as-prepared MnCo2O4/NMCNA exhibited remarkable catalytic performance and outstanding stability for both ORR and OER in alkaline media. The macroporous superstructures play vital role in reducing the ion transport resistance and facilitating the diffusion of gaseous products (O2). Finally, rechargeable Zn–air batteries using the MnCo2O4/NMCNA catalyst displayed appreciably lower overpotentials, higher power density and better stability than commercial Pt/C, thus raising the prospect of functional low-cost, non-precious-metal bifunctional catalysts in metal–air batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...