Environmental stability of 2D anisotropic tellurium containing nanomaterials: anisotropic to isotropic transition†
Abstract
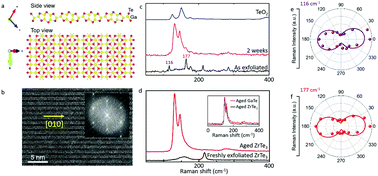
We report on the vibrational (Raman) spectrum and structural transformation of semiconducting pseudo-1D GaTe and ZrTe3 nanomaterials driven by ambient molecular interactions at the nanoscale by angle-resolved Raman spectroscopy, atomic force microscopy (AFM), and environmental X-ray photoelectron (XPS) measurements. The results show that tellurium containing pseudo-1D materials undergo drastic structural and physical changes within a week. During this process, new Raman peaks start to emerge and surface roughness increases substantially. Surprisingly, aged Raman spectra of GaTe, ZrTe3, and α-TeOx show striking similarities suggesting that oxidation of tellurium takes place. Careful, environmental tests reveal that the interaction between GaTe and H2O molecules forms Te–O bonds at the outermost layers of GaTe which leads to newly emerging Raman peaks, a much reduced Schottky junction current density, and an anisotropic to isotropic structural transition. These findings offer fresh interpretation of the aging mechanisms for these material systems, provide new interpretation of the Raman spectrum of aged GaTe which was previously presumed to be of the hexagonal phase, and introduce an anisotropic to isotropic transformation effect induced by molecular interactions on the surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...