In situ assembly of active surface-enhanced Raman scattering substrates via electric field-guided growth of dendritic nanoparticle structures†
Abstract
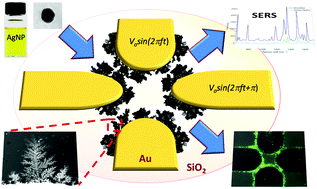
Surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) can provide ultrasensitive detection of chemical and biological analytes down to the level of a single molecule. The need for costly, nanostructured, noble-metal substrates, however, poses a major obstacle in the widespread application of the method. Here we present for the first time a novel type of metallic nanostructured substrates that, not only exhibit a remarkable SERS activity, but are also produced in a facile, cost-effective and nanofabrication-free manner. The substrates are formed through an electric field-guided assembly process of silver nanocolloids, which results in extended and interconnected dendritic nanoparticle structures with a high density of “hot spots”. A unique and significant performance attribute of these nanostructures is their ability to also function as concentration amplification devices, thereby further enhancing their analyte detection efficiency. This major advantage against conventional SERS substrates is illustrated experimentally here with the concentration and detection of proteins from solution. Low limits of detection for illicit drugs, food contaminants and pesticides in relevant matrices are also demonstrated. The SERS-active dendrites are reusable and can be removed and replaced in a few minutes. The SERS substrates presented herein constitute a significant advance towards more effective and less expensive diagnostic tools.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...