Self-assembled hybrid elastin-like polypeptide/silica nanoparticles enable triggered drug release†
Abstract
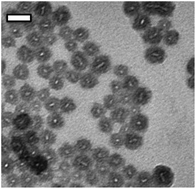
The discovery of biomimetic polypeptides that enable the biomineralization of synthetic and biosynthetic materials has resulted in the development of hybrid materials that incorporate inorganic components for potential application in drug delivery, enzyme immobilization, and surface modification. Here, we describe an approach that uses micellar assemblies of an elastin-like polypeptide (ELP) modified with silica-promoting sequences and drug conjugates that are subsequently encapsulated within a silica matrix. Incorporation of a lysine-rich tag derived from the silaffin R5 peptide into the N-terminus of a hydrophilic ELP that self-assembles upon conjugation of hydrophobic molecules at the C-terminus results in the formation of spherical micelles with a conjugated drug embedded in the core and a corona that is decorated with the silaffin peptide. These micelles serve as the building blocks for the polycondensation of silica into uniform, hybrid polypeptide–silica nanoparticles. We demonstrate proof-of-concept examples using a model hydrophobic small molecule and doxorobucin, a small molecule chemotherapeutic, and further show pH-dependent doxorubicin release from the hybrid nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...