A silica-based SERS chip for rapid and ultrasensitive detection of fluoride ions triggered by a cyclic boronate ester cleavage reaction†
Abstract
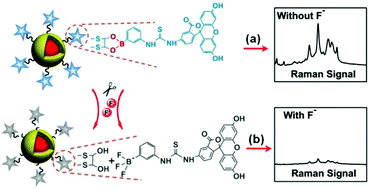
Chemical sensing for the convenient detection of trace aqueous fluoride ions (F−) has been widely explored with the use of various sensing materials and techniques. It still remains a challenge to achieve ultrasensitive but simple, rapid, and inexpensive detection of F− for environmental monitoring and protection. Here we reported a novel surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) nanosensor, fluorescein phenylboronic acid covalently linked to 1,4-dimercapto-2,3-butanediol modified Au@Ag NPs by a cyclic boronate ester (Flu-PBA-Diol-Au@Ag NPs), for the rapid and ultrasensitive detection of F−. Once the Flu-PBA approached the surface of Au@Ag NPs, the Raman signals of Flu-PBA were remarkably enhanced due to the strong SERS effect. However, the presence of F− will induce the cleavage reaction of the cyclic boronate ester into the trifluoroborate anion (3F-Flu-PBA) and diol. The 3F-Flu-PBA molecules exfoliated from the surface of Au@Ag NPs, and the SERS signals of the nanosensor were quenched. Following the sensing mechanism, a silica-based SERS chip has been fabricated by the assembly of Flu-PBA-Diol-Au@Ag NPs on a piece of silicon wafer. The silica-based SERS chips showed high sensitivity for aqueous F−, and the limit of detection (LOD) could reach as low as 0.1 nM. Each test using the SERS chip only needs a droplet of 20 μL sample and is accomplished within ∼10 min. The silica-based SERS chip has also been applied to the quantification of F− in tap water and lake water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...