Assessment of aggregative growth of MnZn ferrite nanoparticles†
Abstract
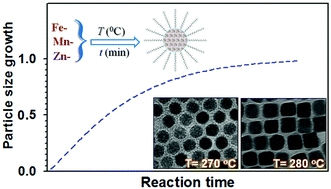
MnZn ferrite (MnZnFe2O4, MZF) nanoparticles (NPs) represent an intriguing class of magnetic NPs in terms of composition-tunable magnetic properties, but the ability to control the size and morphology is essential to exploit such properties. This report describes the findings of an investigation of the size and morphology controllability in terms of growth kinetics of the NPs in a thermochemical synthesis process. MZF NPs of different sizes were synthesized at different temperatures. In addition to shape evolution, the overall size of the as-synthesized magnetic NPs is shown to increase with the reaction temperature and reaction time, revealing that the size growth process can be described by an aggregative growth mechanism. While the apparent rate constant decreases with the reaction temperature, the growth factor remains at 1–2, consistent with a low-dimensionality growth mode. Higher temperature and longer reaction time apparently favor the formation of cubic shapes. The dependence of the overall average particle size on the reaction temperature yields a diffusional activation energy in the order of 10–20 kJ mol−1, a value slightly smaller than those reported for aggregative growth of other types of NPs in solutions. The unravelling of the kinetic parameters provides some new insights into the development of strategies for synthesizing MZF NPs with controllable sizes and shapes.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...