Mapping the local particle plasmon sensitivity with a scanning probe
Abstract
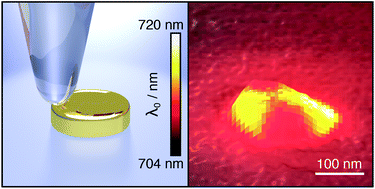
We probe the local sensitivity of an optically excited plasmonic nanoparticle by changing the local dielectric environment through a scanning glass fiber tip. Recording the particle plasmon scattering spectrum for each tip position allows us to observe spectral resonance shifts concurrent with changes in scattering intensity and plasmon damping. For the tip-induced spectral shifts we find the strongest sensitivity at the particle edges, in accordance with the spatial plasmonic field profile. In contrast, the strongest sensitivity occurs at the center of the particle if the scattering intensity is probed at the short wavelength slope of the plasmon resonance instead of the resonance position. This bears important implications for plasmonic sensing, in particular when done at a single light wavelength.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...