The dispersion and aggregation of graphene oxide in aqueous media†
Abstract
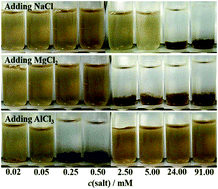
Graphene oxide (GO), as a typical two-dimensional material, possesses a range of oxygen-containing groups and shows surfactant and/or polyelectrolyte-like characteristics. Herein, GO sheets with narrow size distribution were prepared by an ultracentrifugation-based process and the aggregation behaviour of GO in pure water and an electrolyte aqueous solution were studied using laser light scattering (LLS). When adding common electrolytes, such as NaCl and MgCl2, into the GO dispersions, aggregation occurs and irreversible coagulation eventually occurs too. However, the GO dispersion can still remain stable when adding excess AlCl3. The zeta potential of the GO dispersion changes from negative to positive after the addition of access AlCl3, indicating that electrostatic repulsion is still responsible for the dispersion of GO, which is in good agreement with the LLS results. This finding on the dispersion of GO may be applied in the solution processing of GO. It also expands the scope of the design and preparation of new GO-based hybrid materials with different functions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...