Optically active red-emitting Cu nanoclusters originating from complexation and redox reaction between copper(ii) and d/l-penicillamine†
Abstract
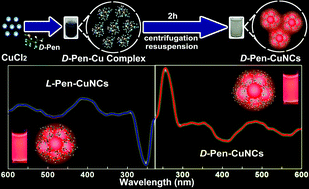
Despite a significant surge in the number of investigations into both optically active Au and Ag nanostructures, there is currently only limited knowledge about optically active Cu nanoclusters (CuNCs) and their potential applications. Here, we have succeeded in preparing a pair of optically active red-emitting CuNCs on the basis of complexation and redox reaction between copper(II) and penicillamine (Pen) enantiomers, in which Pen serves as both a reducing agent and a stabilizing ligand. Significantly, the CuNCs feature unique aggregation induced emission (AIE) characteristics and therefore can serve as pH stimuli-responsive functional materials. Impressively, the ligand chirality plays a dramatic role for the creation of brightly emissive CuNCs, attributed to the conformation of racemic Pen being unfavorable for the electrostatic interaction, and thus suppressing the formation of cluster aggregates. In addition, the clusters display potential toward cytoplasmic staining and labelling due to the high photoluminescence (PL) quantum yields (QYs) and remarkable cellular uptake, in spite that no chirality-dependent effects in autophagy and subcellular localization are observed in the application of chiral cluster enantiomer-based cell imaging.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...