Selective modification of nanoparticle arrays by laser-induced self assembly (MONA-LISA): putting control into bottom-up plasmonic nanostructuring†
Abstract
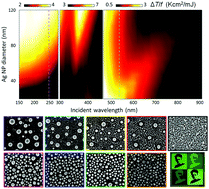
Nano-structuring of metals is one of the greatest challenges for the future of plasmonic and photonic devices. Such a technological challenge calls for the development of ultra-fast, high-throughput and low-cost fabrication techniques. Laser processing, accounts for the aforementioned properties, representing an unrivalled tool towards the anticipated arrival of modules based in metallic nanostructures, with an extra advantage: the ease of scalability. In the present work we take advantage of the ability to tune the laser wavelength to either match the absorption spectral profile of the metal or to be resonant with the plasma oscillation frequency, and demonstrate the utilization of different optical absorption mechanisms that are size-selective and enable the fabrication of pre-determined patterns of metal nanostructures. Thus, we overcome the greatest challenge of Laser Induced Self Assembly by combining simultaneously large-scale character with atomic-scale precision. The proposed process can serve as a platform that will stimulate further progress towards the engineering of plasmonic devices.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...