Epitaxial integration of a nanoscale BiFeO3 phase boundary with silicon
Abstract
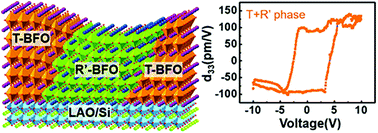
The successful integration of the strain-driven nanoscale phase boundary of BiFeO3 onto a silicon substrate is demonstrated with extraordinary ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism. The detailed strain history is delineated through a reciprocal space mapping technique. We have found that a distorted monoclinic phase forms prior to a tetragonal-like phase, a phenomenon which may correlates with the thermal strain induced during the growth process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...