Carboxylated nanodiamonds inhibit γ-irradiation damage of human red blood cells†
Abstract
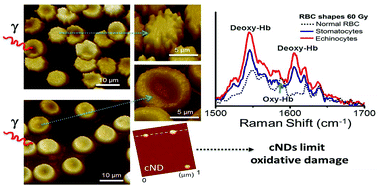
Nanodiamonds when carboxylated (cNDs) act as reducing agents and hence could limit oxidative damage in biological systems. Gamma (γ)-irradiation of whole blood or its components is required in immunocompetent patients to prevent transfusion-associated graft versus host disease (TA-GVHD). However, γ-irradiation of blood also deoxygenates red blood cells (RBCs) and induces oxidative damage, including abnormalities in cellular membranes and hemolysis. Using atomic force microscopy (AFM) and Raman spectroscopy, we examined the effect of cNDs on γ-irradiation mediated deoxygenation and morphological damage of RBCs. γ-Radiation induced several morphological phenotypes, including stomatocytes, codocytes and echinocytes. While stomatocytes and codocytes are reversibly damaged RBCs, echinocytes are irreversibly damaged. AFM images show significantly fewer echinocytes among cND-treated γ-irradiated RBCs. The Raman spectra of γ-irradiated RBCs had more oxygenated hemoglobin patterns when cND-treated, resembling those of normal, non-irradiated RBCs, compared to the non-cND-treated RBCs. cND inhibited hemoglobin deoxygenation and morphological damage, possibly by neutralizing the free radicals generated during γ-irradiation. Thus cNDs have the therapeutic potential to preserve the quality of stored blood following γ-irradiation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...