Upconversion luminescence enhancement in plasmonic architecture with random assembly of metal nanodomes†
Abstract
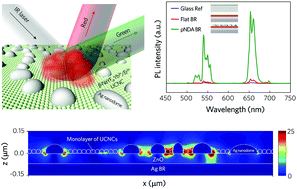
We report an experimental study on the highly enhanced upconversion luminescence (UCL) of β-NaYF4:Yb3+/Er3+ nanocrystals (NCs) in a plasmonic architecture. For the architecture, we designed a thin film device composed of a thin layer of NCs capped with an upper layer of a plasmonic nanodome array (pNDA) and lower substrate of a back reflector (BR). Compared to the UCL intensity observed in a glass reference substrate, the designed plasmonic architecture exhibits distinctively strong luminescence enhanced by up to 800-fold. The intensity considerably exceeds the previously reported luminescence intensity regardless of the excitation power. We elucidated a mechanism explaining the large UCL enhancement, which quantitatively analyzes the combination of plasmonic effects as well as multiple large scattering. More importantly, we provided a detailed analysis of the Ag NDA-derived and BR-assisted plasmonic effects that contribute to an increase in the radiative decay rate and an enhancement of the absorption of incident light. The present study is expected to be beneficial for designing a thin film-based plasmonic structure with a randomized metal nanostructure for high-efficiency photovoltaic devices and infrared detectors.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...