Carboxyl-functionalized polyurethane nanoparticles with immunosuppressive properties as a new type of anti-inflammatory platform†
Abstract
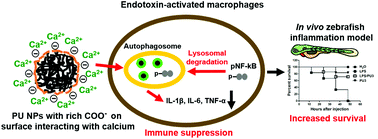
The interaction of nanoparticles (NPs) with the body immune system is critically important for their biomedical applications. Most NPs stimulate the immune response of macrophages. Here we show that synthetic polyurethane nanoparticles (PU NPs, diameter 34–64 nm) with rich surface COO− functional groups (zeta potential −70 to −50 mV) can suppress the immune response of macrophages. The specially-designed PU NPs reduce the gene expression levels of proinflammatory cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α) for endotoxin-treated macrophages. The PU NPs increase the intracellular calcium of macrophages (4.5–6.5 fold) and activate autophagy. This is in contrast to the autophagy dysfunction generally observed upon NP exposure. These PU NPs may further decrease the nuclear factor-κB-related inflammation via autophagy pathways. The immunosuppressive activities of PU NPs can prevent animal death by inhibiting the macrophage recruitment and proinflammatory responses, confirmed by an in vivo zebrafish model. Therefore, the novel biodegradable PU NPs demonstrate COO− dependent immunosuppressive properties without carrying any anti-inflammatory agents. This study suggests that NP surface chemistry may regulate the immune response, which provides a new paradigm for potential applications of NPs in anti-inflammation and immunomodulation.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...