Induction of apoptosis in human cancer cells by targeting mitochondria with gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
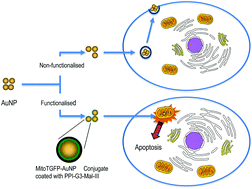
A major challenge in designing cancer therapies is the induction of cancer cell apoptosis, although activation of intrinsic apoptotic pathways by targeting gold nanoparticles to mitochondria is promising. We report an in vitro procedure targeting mitochondria with conjugated gold nanoparticles and investigating effects on apoptosis induction in the human breast cancer cell line Jimt-1. Gold nanoparticles were conjugated to a variant of turbo green fluorescent protein (mitoTGFP) harbouring an amino-terminal mitochondrial localization signal. Au nanoparticle conjugates were further complexed with cationic maltotriose-modified poly(propylene imine) third generation dendrimers. Fluorescence and transmission electron microscopy revealed that Au nanoparticle conjugates were directed to mitochondria upon transfection, causing partial rupture of the outer mitochondrial membrane, triggering cell death. The ability to target Au nanoparticles into mitochondria of breast cancer cells and induce apoptosis reveals an alternative application of Au nanoparticles in photothermal therapy of cancer.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...