Glutathione- and pH-responsive nonporous silica prodrug nanoparticles for controlled release and cancer therapy†
Abstract
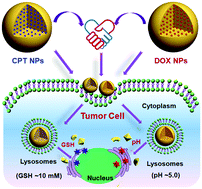
A myriad of drug delivery systems such as liposomes, micelles, polymers and inorganic nanoparticles (NPs) have been developed for cancer therapy. Very few of them, however, have the ability to integrate multiple functionalities such as specific delivery, high circulation stability, controllable release and good biocompatibility and biodegradability in a single system to improve the therapeutic efficacy. Herein, we report two types of stimuli-responsive nonporous silica prodrug NPs towards this goal for controlled release of anticancer drugs and efficient combinatorial cancer therapy. As a proof of concept, anticancer drugs camptothecin (CPT) and doxorubicin (DOX) were covalently encapsulated into silica matrices through glutathione (GSH)-responsive disulfide and pH-responsive hydrazone bonds, respectively, resulting in NPs with sizes tunable in the range of 50–200 nm. Both silica prodrug NPs showed stimuli-responsive controlled release upon exposure to a GSH-rich or acidic environment, resulting in improved anticancer efficacy. Notably, two prodrug NPs simultaneously taken up by HeLa cells showed a remarkable combinatorial efficacy compared to free drug pairs. These results suggest that the stimuli-responsive silica prodrug NPs are promising anticancer drug carriers for efficient cancer therapy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...