Smart doxorubicin nanoparticles with high drug payload for enhanced chemotherapy against drug resistance and cancer diagnosis†
Abstract
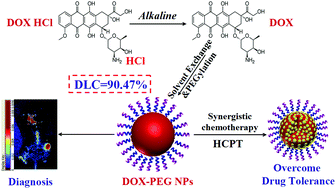
Considering the obvious advantages in efficacy and price, doxorubicin (DOX) has been widely used for a range of cancers, which is usually encapsulated in various nanocarriers for drug delivery. Although effective, in most nanocarrier-based delivery systems, the drug loading capacity of DOX is rather low; this can lead to undesired systemic toxicity and excretion concern. Herein, we report for the first time the usage of pure doxorubicin nanoparticles (DOX NPs) without addition of any carriers for enhanced chemotherapy against drug-resistance. The drug payload reaches as high as 90.47%, which largely surpassed those in previous reports. These PEG stabilized DOX NPs exhibit good biocompatibility and stability, long blood circulation time, fast release in an acidic environment and high accumulation in tumors. Compared with free DOX, DOX NPs display a dramatically enhanced anticancer therapeutic efficacy in the inhibition of cell and tumor growth. Moreover, they can also be readily incorporated with other anticancer drugs for synergistic chemotherapy to overcome the drug resistance of cancers. The fluorescence properties of DOX also endow these NPs with imaging capabilities, thus making it a multifunctional system for diagnosis and treatment. This work demonstrates great potential of DOX NPs for cancer diagnosis, therapy and overcoming drug tolerance.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...