Polyelectrolyte-coated gold nanorods and their biomedical applications
Abstract
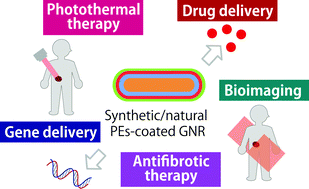
Gold nanorods (GNRs) have been extensively used in biomedical applications, because of their favourable optical properties. Their longitudinal surface plasmon resonance can be tuned, providing a strong near-infrared (NIR) extinction coefficient peak within the tissue transparency window. However, the modification of the surface of GNRs is essential before they can be used for biomedical applications. The number of GNRs taken up by cells and their biodistribution depend on their surface modification. Here, we review the recent advances in modifying GNR surfaces with polyelectrolytes for biomedical applications. Major polyelectrolytes used to coat GNR surfaces over the past few years and the biocompatibility of polyelectrolyte-coated GNRs are discussed.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...