Small angle X-ray scattering coupled with in situ electromechanical probing of nanoparticle-based resistive strain gauges†
Abstract
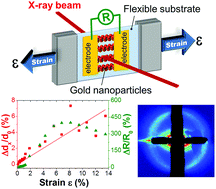
A comprehensive study on the electromechanical behavior of nanoparticle-based resistive strain gauges in action through normal and grazing incidence small angle X-ray scattering (SAXS/GISAXS) investigations is presented. The strain gauges were fabricated from arrays of colloidal gold nanoparticle (NP) wires assembled on flexible polyethylene terephthalate and polyimide substrates by convective self-assembly. Microstructural changes (mean interparticle distance variations) within these NP wires under uniaxial stretching estimated by SAXS/GISAXS are correlated to their macroscopic electrical resistance variations. SAXS measurements suggest a linear longitudinal extension and transversal contraction of the NP wires with applied strain (0 to ∼13%). The slope of this longitudinal variation is less than unity, implying a partial strain transfer from the substrate to the NP wires. The simultaneously measured electrical resistance of the strain gauges shows an exponential variation within the elastic domain of the substrate deformation, consistent with electron tunnelling through the interparticle gaps. A slower variation observed within the plastic domain suggests the formation of new electronic conduction pathways. Implications of transversal contraction of the NP wires on the directional sensitivities of strain gauges are evaluated by simulating electronic conduction in models mimicking a realistic NP arrangement. A loss of directionality of the NP-based strain gauges due to transversal current flow within the NP wires is deduced.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...