pH dependent catalytic activities of platinum nanoparticles with respect to the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide and scavenging of superoxide and singlet oxygen†
Abstract
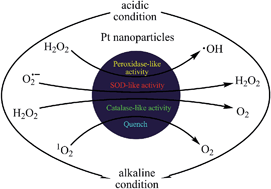
Recently, platinum (Pt) nanoparticles (NPs) have received increasing attention in the field of catalysis and medicine due to their excellent catalytic activity. To rationally design Pt NPs for these applications, it is crucial to understand the mechanisms underlying their catalytic and biological activities. This article describes a systematic study on the Pt NP-catalyzed decomposition of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and scavenging of superoxide (O2˙−) and singlet oxygen (1O2) over a physiologically relevant pH range of 1.12–10.96. We demonstrated that the catalytic activities of Pt NPs can be modulated by the pH value of the environment. Our results suggest that Pt NPs possess peroxidase-like activity of decomposing H2O2 into ˙OH under acidic conditions, but catalase-like activity of producing H2O and O2 under neutral and alkaline conditions. In addition, Pt NPs exhibit significant superoxide dismutase-like activity of scavenging O2˙− under neutral conditions, but not under acidic conditions. The 1O2 scavenging ability of Pt NPs increases with the increase in the pH of the environment. The study will provide useful guidance for designing Pt NPs with desired catalytic and biological properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...