Low-temperature CVD synthesis of patterned core–shell VO2@ZnO nanotetrapods and enhanced temperature-dependent field-emission properties
Abstract
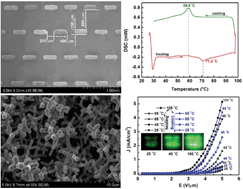
VO2 nanostructures are attractive materials because of their reversible metal–insulator transition (MIT) and wide applications in devices. When they are used as field emitters, a new type of temperature-controlled field emission device can be fabricated. Vapor transport methods used to synthesize traditional VO2 nanostructures are energy-intensive, low yield, and produce simple morphology (quasi-1D) that exhibits substrate clamping; thus they are not suitable for field emission applications. To overcome these limitations, ZnO nanotetrapods were used as templates, and patterned core–shell VO2@ZnO nanotetrapods were successfully grown on an ITO/glass substrate via a low-temperature CVD synthesis. SEM, TEM, EDX, XPS analyses and X-ray diffraction revealed that the cores and shells of these nanotetrapods were single crystal wurtzite-type ZnO and polycrystalline VO2, respectively. The VO2@ZnO nanotetrapods show strongly MIT-related FE properties, the emission current density at low temperature is significantly enhanced in comparison with pure VO2 nanostructures, and the emission current density increased by about 20 times as the ambient temperature increased from 25 to 105 °C at a fixed field of 5 V μm−1. Although the VO2@ZnO nanotetrapods show a worse FE performance at low temperatures compared with pure ZnO nanotetrapods, the FE performance was substantially improved at high temperatures, which was attributed to the MIT-related band bending near the interface and the abrupt resistance change across the MIT.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...