Ligand effect on the size, valence state and red/near infrared photoluminescence of bidentate thiol gold nanoclusters†
Abstract
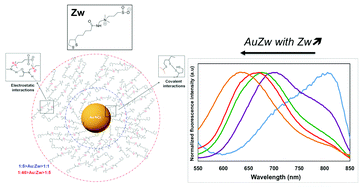
Synthesis and characterization of gold nanoclusters (Au NCs) stabilized by a zwitterion ligand (Zw) at different Au : Zw ratios are demonstrated. Au NCs exhibit photoluminescence (PL) emission which is tunable from the near infrared (805 nm) to the red spectral window (640 nm) and strongly influenced by the ligand shell size. Optical and chemical investigations suggest the presence of gold polymeric species and large nanoclusters for a molar ratio of Au : Zw = 1 : 1. For 1 : 5 < Au : Zw < 1 : 1, Zw induces etching of the large clusters and the formation of a monolayer of the bidentate ligands on the Au NCs (cluster size ∼7 to 10 kDa) accompanied by red PL emission at λ = 710 nm. A second organic layer starts to form for larger Zw fractions (Au : Zw < 1 : 5) as a result of electrostatic and covalent interactions of the zwitterion leading to an enhancement and a blue-shift of the PL emission. The effect of temperature and pH on the optical properties of gold clusters is strongly dependent on the ligand shell and demonstrates the importance of defining gold nanoclusters as supramolecular assemblies with a complex environment.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...