An efficient one-step condensation and activation strategy to synthesize porous carbons with optimal micropore sizes for highly selective CO2 adsorption†
Abstract
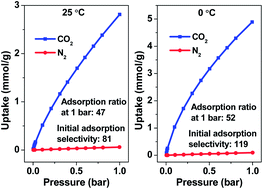
A series of microporous carbons (MPCs) were successfully prepared by an efficient one-step condensation and activation strategy using commercially available dialdehyde and diamine as carbon sources. The resulting MPCs have large surface areas (up to 1881 m2 g−1), micropore volumes (up to 0.78 cm3 g−1), and narrow micropore size distributions (0.7–1.1 nm). The CO2 uptakes of the MPCs prepared at high temperatures (700–750 °C) are higher than those prepared under mild conditions (600–650 °C), because the former samples possess optimal micropore sizes (0.7–0.8 nm) that are highly suitable for CO2 capture due to enhanced adsorbate–adsorbent interactions. At 1 bar, MPC-750 prepared at 750 °C demonstrates the best CO2 capture performance and can efficiently adsorb CO2 molecules at 2.86 mmol g−1 and 4.92 mmol g−1 at 25 and 0 °C, respectively. In particular, the MPCs with optimal micropore sizes (0.7–0.8 nm) have extremely high CO2/N2 adsorption ratios (47 and 52 at 25 and 0 °C, respectively) at 1 bar, and initial CO2/N2 adsorption selectivities of up to 81 and 119 at 25 °C and 0 °C, respectively, which are far superior to previously reported values for various porous solids. These excellent results, combined with good adsorption capacities and efficient regeneration/recyclability, make these carbons amongst the most promising sorbents reported so far for selective CO2 adsorption in practical applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...