Random telegraph noise and resistance switching analysis of oxide based resistive memory†
Abstract
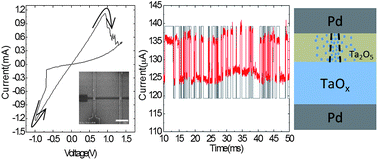
Resistive random access memory (RRAM) devices (e.g. “memristors”) are widely believed to be a promising candidate for future memory and logic applications. Although excellent performance has been reported, the nature of resistance switching is still under extensive debate. In this study, we perform systematic investigation of the resistance switching mechanism in a TaOx based RRAM through detailed noise analysis, and show that the resistance switching from high-resistance to low-resistance is accompanied by a semiconductor-to-metal transition mediated by the accumulation of oxygen-vacancies in the conduction path. Specifically, pronounced random-telegraph noise (RTN) with values up to 25% was observed in the device high-resistance state (HRS) but not in the low-resistance state (LRS). Through time-domain and temperature dependent analysis, we show that the RTN effect shares the same origin as the resistive switching effects, and both can be traced to the (re)distribution of oxygen vacancies (VOs). From noise and transport analysis we further obtained the density of states and average distance of the VOs at different resistance states, and developed a unified model to explain the conduction in both the HRS and the LRS and account for the resistance switching effects in these devices. Significantly, it was found that even though the conduction channel area is larger in the HRS, during resistive switching a localized region gains significantly higher VO and dominates the conduction process. These findings reveal the complex dynamics involved during resistive switching and will help guide continued optimization in the design and operation of this important emerging device class.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...