Highly sensitive free radical detection by nitrone-functionalized gold nanoparticles†
Abstract
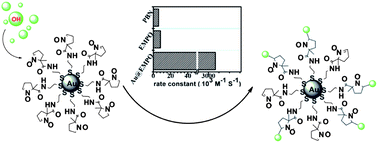
The detection of free radicals and related species has attracted significant attention in recent years because of their critical roles in physiological and pathological processes. Among the methods for the detection of free radicals, electron spin resonance (ESR) coupled with the use of the spin trapping technique has been an effective approach for characterization and quantification of these species due to its high specificity. However, its application in biological systems, especially in in vivo systems, has been greatly limited partially due to the low reaction rate between the currently available spin traps with biological radicals. To overcome this drawback, we herein report the first example of nitrone functionalized gold nanoparticles (Au@EMPO) as highly efficient spin traps in which the thiolated EMPO (2-(ethoxycarbonyl)-2-methyl-3,4-dihydro-2H-pyrrole 1-oxide) derivative was self-assembled on gold nanoparticles. Kinetic studies showed that Au@EMPO has a 137-fold higher reaction rate constant with ˙OH than PBN (N-tert-butyl-α-phenylnitrone). Owing to the high rate of trapping ˙OH by Au@EMPO as well as the high stability of the resulting spin adduct (t1/2 ∼ 56 min), Au@EMPO affords 124-fold higher sensitivity for ˙OH than EMPO. Thus, this new nanospin trap shows great potential in trapping the important radicals such as ˙OH in various biological systems and provides a novel strategy to design spin traps with much improved properties.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...