Penetration and lateral diffusion characteristics of polycrystalline graphene barriers†
Abstract
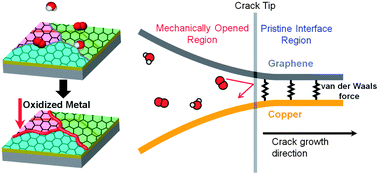
We report penetration and lateral diffusion behavior of environmental molecules on synthesized polycrystalline graphene. Penetration occurs through graphene grain boundaries resulting in local oxidation. However, when the penetrated molecules diffuse laterally, the oxidation region will expand. Therefore, we measured the lateral diffusion rate along the graphene–copper interface for the first time by the environment-assisted crack growth test. It is clearly shown that the lateral diffusion is suppressed due to the high van der Waals interaction. Finally, we employed bilayer graphene for a perfect diffusion barrier facilitated by decreased defect density and increased lateral diffusion path.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...