Multiplex acute leukemia cytosensing using multifunctional hybrid electrochemical nanoprobes at a hierarchically nanoarchitectured electrode interface†
Abstract
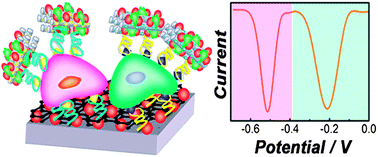
We have developed a robust, nanobiotechnology-based electrochemical cytosensing approach with high sensitivity, selectivity, and reproducibility toward the simultaneous multiplex detection and classification of both acute myeloid leukemia and acute lymphocytic leukemia cells. The construction of the electrochemical cytosensor involves the hierarchical assembly of dual aptamer-functionalized, multilayered graphene–Au nanoparticle electrode interface and the utilization of hybrid electrochemical nanoprobes co-functionalized with redox tags, horseradish peroxidase, and cell-targeting nucleic acid aptamers. The hybrid nanoprobes are multifunctional, capable of specifically targeting the cells of interest, amplifying the electrochemical signals, and generating distinguishable signals for multiplex cytosensing. The as-assembled electrode interface not only greatly facilitates the interfacial electron transfer process due to its high conductivity and surface area but also exhibits excellent biocompatibility and specificity for cell recognition and adhesion. A superstructured sandwich-type sensor geometry is adopted for electrochemical cytosensing, with the cells of interest sandwiched between the nanoprobes and the electrode interface. Such an electrochemical sensing strategy allows for ultrasensitive, multiplex acute leukemia cytosensing with a detection limit as low as ∼350 cells per mL and a wide linear response range from 5 × 102 to 1 × 107 cells per mL for HL-60 and CEM cells, with minimal cross-reactivity and interference from non-targeting cells. This electrochemical cytosensing approach holds great promise as a new point-of-care diagnostic tool for early detection and classification of human acute leukemia and may be readily expanded to multiplex cytosensing of other cancer cells.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...