Microscopy and tunable resistive pulse sensing characterization of the swelling of pH-responsive, polymeric expansile nanoparticles†
Abstract
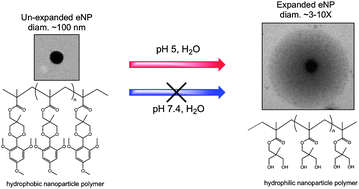
Polymeric expansile nanoparticles (eNPs) that respond to a mildly acidic environment by swelling with water and expanding 2–10× in diameter represent a new responsive drug delivery system. Here, we use a variety of techniques to characterize the pH- and time-dependence of eNP swelling as this is a key property responsible for the observed in vitro and in vivo performance of eNPs. Results demonstrate a significant change in eNP volume (>350×) at pH 5.0 as seen using: scanning electron microscopy (SEM), conventional transmission electron microscopy (TEM), freeze-fracture transmission electron microscopy (ff-TEM), fluorescence microscopy, and a new nanopore based characterization technology, the qNano, which measures both individual particle size as well as overall particle concentration in situ using tunable resistive pulse sensing. eNP swelling occurs in a continuous and yet heterogeneous manner over several days and is pH dependent.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...