Biosensor based on Prussian blue nanocubes/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite for detection of organophosphorus pesticides
Abstract
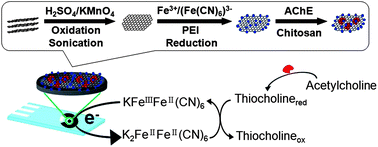
We demonstrate a facile procedure to efficiently prepare Prussian blue nanocubes/reduced graphene oxide (PBNCs/rGO) nanocomposite by directly mixing Fe3+ and [Fe(CN)6]3− in the presence of GO in polyethyleneimine aqueous solution, resulting in a novel acetylcholinesterase (AChE) biosensor for detection of organophosphorus pesticides (OPs). The obtained nanocomposite was characterized by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray (EDX) microanalysis. It was clearly observed that the nanosheet has been decorated with cubic PB nanoparticles and nearly all the nanoparticles are distributed uniformly only on the surface of the reduced GO. No isolated PB nanoparticles were observed, indicating the strong interaction between PB nanocubes and the reduced GO and the formation of PBNCs/rGO nanocomposite. The obtained PBNCs/rGO based AChE biosensor make the peak potential shift negatively to 220 mV. The over-potential decreases ∼460 mV compared to that on a bare electrode, suggesting that PBNCs/rGO has a high electrocatalytic activity towards the oxidation of thiocholine. The AChE biosensor shows rapid response and high sensitivity for detection of monocrotophos with a linear range from 1.0 to 600 ng mL−1 and a detection limit of 0.1 ng mL−1. These results suggest that the PBNCs/rGO hybrids nanocomposite exhibited high electrocatalytic activity towards the oxidation of thiocholine, which lead to the sensitive detection of OP pesticides.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...