Bifunctional antimicrobial conjugates and hybrid antimicrobials
Abstract
Covering: up to the end of 2016
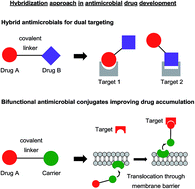
Novel antimicrobial drugs are continuously needed to counteract bacterial resistance development. An innovative molecular design strategy for novel antibiotic drugs is based on the hybridization of an antibiotic with a second functional entity. Such conjugates can be grouped into two major categories. In the first category (antimicrobial hybrids), both functional elements of the hybrid exert antimicrobial activity. Due to the dual targeting, resistance development can be significantly impaired, the pharmacokinetic properties can be superior compared to combination therapies with the single antibiotics, and the antibacterial potency is often enhanced in a synergistic manner. In the second category (antimicrobial conjugates), one functional moiety controls the accumulation of the other part of the conjugate, e.g. by mediating an active transport into the bacterial cell or blocking the efflux. This approach is mostly applied to translocate compounds across the cell envelope of Gram-negative bacteria through membrane-embedded transporters (e.g. siderophore transporters) that provide nutrition and signalling compounds to the cell. Such ‘Trojan Horse’ approaches can expand the antibacterial activity of compounds against Gram-negative pathogens, or offer new options for natural products that could not be developed as standalone antibiotics, e.g. due to their toxicity.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Novel Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Resistance


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...