Structure and thermal stability of sodium and carbonate-co-substituted strontium hydroxyfluorapatites
Abstract
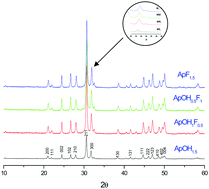
The present study was aimed at investigating the co-substitution of sodium and carbonate in strontium hydroxyfluorapatites because these compounds have many similarities to the mineral phase of bones. Herein, three series of sodium- and carbonate-doped strontium hydroxyfluorapatites were prepared via a co-precipitation method. Chemical analysis via inductively coupled plasma-atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES), X-ray diffraction (XRD), Rietveld refinement, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), 31P nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), and differential and gravimetric thermal analysis (DTA–GTA) characterizations were employed for the identification of the obtained products. Sodium- and fluoride-doped strontium hydroxyapatite was found to be a pure apatitic phase containing ionic vacancies. Rietveld analysis showed a significant decrease in the a lattice parameter as sodium and fluoride levels increased, whereas in carbonate- and fluoride-doped strontium hydroxyapatite, both the a and the c lattice parameters decreased as the amounts of carbonate that were added increased. The obtained powders were a B-type carbonate apatite with vacancies. The co-substitution of sodium and carbonate in the hydroxyfluorapatite structure typically gave rise to B-type carbonate apatite with vacancies. Thermal investigation in the range of 500–1200 °C revealed that decomposition occurred at a temperature of about 800 °C, and Sr3(PO4)2 was formed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...