Facile synthesis of microporous sulfur-doped carbon spheres as electrodes for ultrasensitive detection of ascorbic acid in food and pharmaceutical products†
Abstract
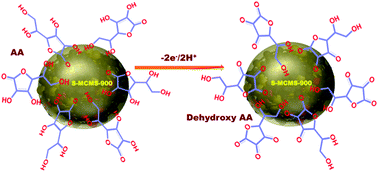
Fabrication of electrodes based on a metal-free catalyst with desirable sensitivity, selectivity, and stability has been given considerable interest. Microporous sulfur-doped carbon microspheres (S-MCMS) were synthesized and assembled as an electrochemical sensor for the monitoring of ascorbic acid (AA) in commercial juices and vitamin C tablets. The S-doped microporous carbon with a spherical structure was fabricated at different annealing temperatures (700, 800, and 900 °C) to achieve a high surface area, an actively doped carbon interfacial surface, soft interactive surfaces and an open microporous network. The high surface area, actively doped S-atom percentage, microporous construction, and active doping of the carbon microsphere construction of S-MCMS-900, make it a highly stable metal-free electrocatalyst for selective detection of AA. The S-atoms incorporated with the sp2-carbon matrix form numerous active sites, which bind to targets and stimulate the transduction of the electrochemical interaction with a fast response and high charge transfer efficiency. Selective monitoring of AA on S-MCMS-900 with high sensitivity was achieved with a detection limit as low as 1 μM, and wide linear range up to 4 mM. Monitoring of AA in lemon juice or pharmaceutical tablets was realized by using S-MCMS-900, with a fast response, high sensitivity, reliable selectivity, high stability and rational reproducibility. S-MCMS-900 can be employed as a fast, sensitive, and selective assay for routine detection of AA in food, biological, and environmental samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...