A novel ESIPT-based fluorescent chemodosimeter for Hg2+ detection and its application in live-cell imaging†
Abstract
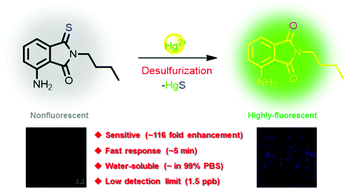
A new excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) based fluorescent chemodosimeter for the detection of Hg2+ has been rationally designed and developed. The probe operates via the specific mercury-promoted desulfurization reaction of thiophthalimide to phthalimide and exhibits high selectivity and sensitivity in an almost pure aqueous solution (containing only 1% DMSO) with a low detection limit of 1.5 ppb. Furthermore, the probe was successfully used for the fluorescence imaging of Hg2+ in live cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...