Molecular hybrid design, synthesis and biological evaluation of N-phenyl sulfonamide linked N-acyl hydrazone derivatives functioning as COX-2 inhibitors: new anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and anti-bacterial agents†
Abstract
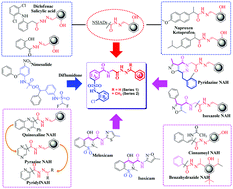
Herein, we report the design, synthesis and biological evaluation of the anti-inflammatory activities of N-phenyl sulfonamide linked N-acylhydrazones (NPS–NAH), using the molecular hybridization approach. Hybrid compounds were further validated by theoretical studies. Compound 1f from series-1 and compound 2a from series-2 exhibited strong selective COX-2 enzyme inhibition at IC50 = 8.9 μM and 8.4 μM respectively. Effective in vivo anti-inflammatory profiling of potent and selective COX-2 inhibitors, including compound 1f and 2a was carried out and compared with known COX-2 inhibitors. Subsequently, these compounds were tested for antioxidant activity, and 1h (IC50 = 28.62 μM) from series-1 and compound 2d (IC50 = 25.34 μM) from series-2 were found to be potent anti-oxidants. Additionally, these compounds were screened for antibacterial activity, and compound 1l and 2b exhibited better Gram +ve and −ve anti-bacterial activity than the reference standards, Ciprofloxacin and Norfloxacin. These results validated the idea of exploiting the hybridization strategy for the identification of new N-phenyl sulfonamide–NAH derivatives for optimizing anti-inflammatory, antioxidant and anti-bacterial activities.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...