Construction of a selective electrochemical sensing solid–liquid interface for the selective detection of fluoride ion in water with bis(indolyl)methane-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes†
Abstract
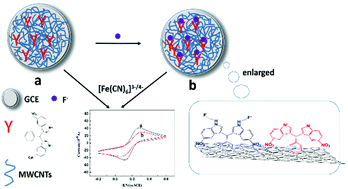
Based on the fluoride ion recognition ability of nitro-substituted 3,3′-bis(indolyl)methane (Nbim) and unique properties of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) with enlarged active surface area and high electrical conductivity, a new solid–liquid interface for the selective detection of fluoride ion in water was fabricated by a Nbim/MWCNT-modified glassy carbon electrode. To transform the molecular interactions occurring at the solid liquid interface into measurable signals, electrochemical techniques were used through the electron transfer mediator of K3Fe(CN)6. Because of the synergistic effect of Nbim and MWCNTs, the as-prepared electrochemical sensing interface can be applied for the selective voltammetric determination of non-electroactive analytes (F−) based on the changes in the peak currents of the ferricyanide/ferrocyanide couple. The response current was linear, with F− concentration in the range from 1 μM to 130 μM and a detection limitation of 0.1 μM. This study offers a new strategy for the detection F− by a solid interface in practical water samples.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...