Direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate from CO2 and methanol over CaO–CeO2 catalysts: the role of acid–base properties and surface oxygen vacancies
Abstract
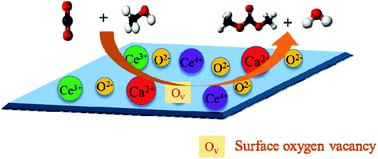
Herein, the direct synthesis of dimethyl carbonate (DMC) from CO2 and methanol was investigated over a series of CeO2-based catalysts promoted by variable amounts of CaO. The catalysts were synthesized by a co-precipitation method and fully characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 adsorption/desorption, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and NH3-TPD and CO2-TPD techniques. The results demonstrated that the addition of different amounts of CaO could affect the structure and surface properties of the obtained catalysts. The acid–base properties and amount of surface oxygen vacancies on the surface of the catalysts were improved due to the interaction between CaO and CeO2, and the oxygen vacancies enhanced the adsorption of CO2. The synthesis of DMC from CO2 and methanol was studied in a slurry bed reactor at 3 MPa and 140 °C. The results revealed that the acid–base properties and oxygen vacancies play a crucial role in promoting the formation of DMC. Among all the bimetallic and pure CeO2 catalysts, the Ca1.5Ce sample showed the maximum DMC yield (2.47 mmol g−1) due to the modification of the acid–base properties of the catalyst and the existence of higher concentration of oxygen vacancies on the CeO2 surface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...