Inner surface modification of 1.76 nm diameter (13,13) carbon nanotubes and the desalination behavior of its reverse osmosis membrane
Abstract
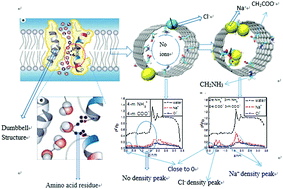
Since wide carbon nanotubes (CNTs) have higher water flux and are less expensive than narrow ones, a set of RO membranes with modified CNTs of 1.76 nm in diameter (13,13) were built in this work, and the mechanisms of water flux and salt rejection were studied through molecular dynamics simulations. In this paper, oppositely-charged functional groups (–CH2COO− and –CH2NH3+) were added to the interior of the CNTs to construct a throat similar to the protein Aquaporin-4. The conductance, potential of the mean force and density distribution of ions in the CNTs were examined. In this study, the results show that salt rejection of CNTs inner-modified with oppositely-charged groups can be dramatically improved under 200 MPa. CNTs modified inside with four −CH2COO−/–CH2NH3+ functional group pairs could lead to 100% salt rejection. CNTs modified both in the interior and at the entrance with oppositely-charged functional groups could achieve both 100% desalination and high water conduction. Compared to those with only four functional group pairs in the interior, CNTs with three –CH2COO−/–CH2NH3+ pairs in the interior and one or two pairs at the entrance led to 100% desalination with a 12% increase in water flux. The water flux of the functionalized (13,13) CNTs was 3.4 times as high as that in (8,8) CNTs, although it declined to 54% compared to unfunctionalized (13,13) CNTs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...