Photoluminescence properties and preferable site occupancy of Ce3+ in apatite-like RbSr4(BO3)3 blue-emitting phosphors for white LEDs†
Abstract
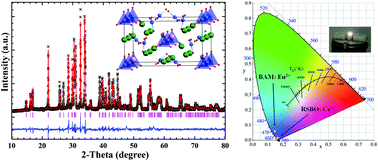
A near-ultraviolet (n-UV) pumped blue-emitting apatite-like phosphor RbSr4(BO3)3:Ce3+ (RSBO:Ce3+) was synthesized using a high temperature solid-state reaction method. Rietveld refinement on the structure indicates that Ce3+ ions are apt to occupy the Sr12+ (8c) site, in spite of one Rb+ and three different crystallographic Sr2+ ions in the structure. The Ce3+ ion activated RbSr4(BO3)3 (RSBO) material can be excited by a relatively broad absorption band ranging from 320 to 365 nm, which matches well with the light from the commercial n-UV white light emitting diode (w-LED) chips, and generates a strong blue emission spectrum peaking at 415 nm due to the electronic transitions from 5d to 4f of the Ce3+ ion. And the color purity of RSBO:Ce3+ is comparable to that of the blue-emitting commercial phosphor BAM:Eu2+. The temperature-dependent spectra show that its luminescence intensity at 100 °C can remain about 85% of the initial value at room temperature. A w-LED device was fabricated by combining the RSBO:Ce3+, commercial (Sr,Ba)2SiO4:Eu2+ and (Ca,Sr)SiAlN3:Eu2+ phosphors with a 365 nm n-UV chip. The w-LED device generates white light with CIE chromaticity coordinates, correlated color temperature (CCT) and color-rendering index Ra are (x, y) = (0.3315, 0.3402), 5540 K and 72.9, respectively. The experimental results indicate that the RSBO:Ce3+ phosphor is a promising candidate as a blue component for application in w-LEDs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...