Molecular mechanism of tobramycin with human serum albumin for probing binding interactions: multi-spectroscopic and computational approaches†
Abstract
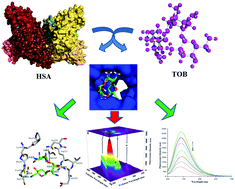
Binding interactions between human serum albumin (HSA) and tobramycin (TOB) under simulated physiological conditions (pH = 7.4) were explored using ultraviolet-visible absorption (UV), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), circular dichroism (CD), and fluorescence, as well as by computational modeling. Fluorescence quenching of HSA upon TOB addition was found to be a static quenching process, as revealed from the diminishing trend of the Stern–Volmer quenching constant with increasing temperature as well as UV-vis absorption spectral results. Fluorescence quenching value as titration results demonstrated an excellent binding affinity with binding constant Ks (2.06 × 106 M−1) between TOB and HSA. The FTIR and the CD spectra showed secondary and tertiary structural changes in the HSA, whereas three-dimensional fluorescence spectral results disclosed microenvironmental perturbations around aromatic fluorophores upon TOB binding. Competitive site-marker displacement results along with molecular modeling suggested the preferred location of the TOB binding site to be site I, located in subdomain IIA of HSA. The solvent accessible surface area (ASAs) calculations for the native HSA and HSA–TOB displayed a reduction in ASAs, providing strong support for effectiveness of TOB binding to HSA. These findings provide a useful experimental strategy for drug designers to further study the molecular binding mechanisms of TOB to HSA to gain better therapeutic efficacy.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...