Synthesis, structures and magnetism of heterotrimetallic Ni–Cu–Ln complexes based on a dicompartmental imine–oxime ligand†
Abstract
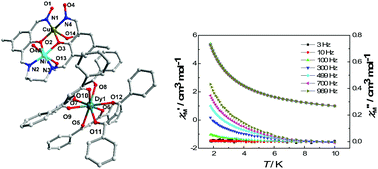
Four NiII–CuII–LnIII heterotrimetallic complexes [Ni(MeOH)(HL)Cu(MeOH)]2[Ln(dbm)4]2·xCH3OH·yH2O (Ln = Gd, x = 4, y = 2 for 1, Ln = Tb, x = 6, y = 0 for 2, Ln = Dy, x = 6, y = 0 for 3, Ln = Ho, x = 6, y = 0 for 4, respectively, H4L = N,N-bis(2-hydroxy-3-hydroxyiminomethyl-5-methylphenylmethylene)-1,3-propanediamine, dbm− = anion of 1,3-diphenyl-propane-1,3-dione) have been synthesized. Structural analyses reveal that in all complexes, NiII and CuII ions are embedded in the dicompartmental imine–oxime ligand of HL to form a [Ni(MeOH)(HL)Cu(MeOH)]+ cation, and the cation itself dimerizes via two oxime oxygen atoms coordinated to Ni(II) ions to form a centrosymmetric tetranuclear cluster of [Ni(MeOH)(HL)Cu(MeOH)]22+. LnIII ions are coordinated by four dbm− anions to form a [Ln(dbm)4]− unit as a balance anion. Magnetic susceptibility measurements show that strong antiferromagnetic couplings are operative between NiII and CuII ions by phenolate and oximato bridges. Ac susceptibility measurements under zero dc-applied field disclose that the Dy derivative behaves as a SMM with a small effective energy of 0.78 K.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...